Dna Ligase Function In Dna Replication | Initiation is the only phase of replication that is regulated, but the mechanism is not yet well understood. The method used to replicate dna in which the telomerase: The dna in these cells are not in nice little rings; James hadfield, cruk cambridge research institute, robinson way, cambridge cb2 0re. Dna replication must occur only once in each cell cycle.
This leads to the formation of two. The encoded protein functions in dna replication, recombination, and the base excision repair process. Jump to navigationjump to search. The enzyme that carries out the replication, dna polymerase, only functions in the 5' to 3' direction. Dna ligase iv (lig4) syndrome is a rare autosomal recessive disorder, manifesting with variable immune deficiency, growth failure, predisposition to malignancy, and cellular sensitivity to dna ligases are indispensable in various dna repair and replication processes and a deficiency or.
Therefore, dna replication requires that the dna is loosened and the double helix is unwound. This protein may act to stop replication by preventing helicase (dnab) from unwinding duplex dna, thereby interrupting the function of the. You do not need to be a curator in order to contribute. Mechanisms to correct errors during dna replication and to repair dna damage over the cell's lifetime. The dna ligase catalyzes the formation of covalent phosphodiester linkages, which permanently join the nucleotides together. This type of replication is called discontinuous. Dna ligase is a specific type of enzyme, a ligase, (ec 6.5.1.1) that facilitates the joining of dna strands together by catalyzing the formation of a phosphodiester bond. The dna in these cells are not in nice little rings; This is the currently selected item. Relaxes the dna helix during replication through creation of a nick in one of the dna strands. It forms the replication fork by breaking hydrogen bonds between nucleotide pairs in dna. Dna replication ends when oppositely advancing forks meet (usually at t1 or t2). Α, ε, δ are dna replicating polymerases, while γ functions in mitochondria to replicate mitochondrial dna.
Dna replication is semi conservative. Dna ligase functions by forming a bond between the end of a donor nucleotide and the end of an acceptor nucleotide. Mechanisms to correct errors during dna replication and to repair dna damage over the cell's lifetime. In addition to replication they also play an important role in dna repair and recombination. However, dna polymerases cannot start dna synthesis.
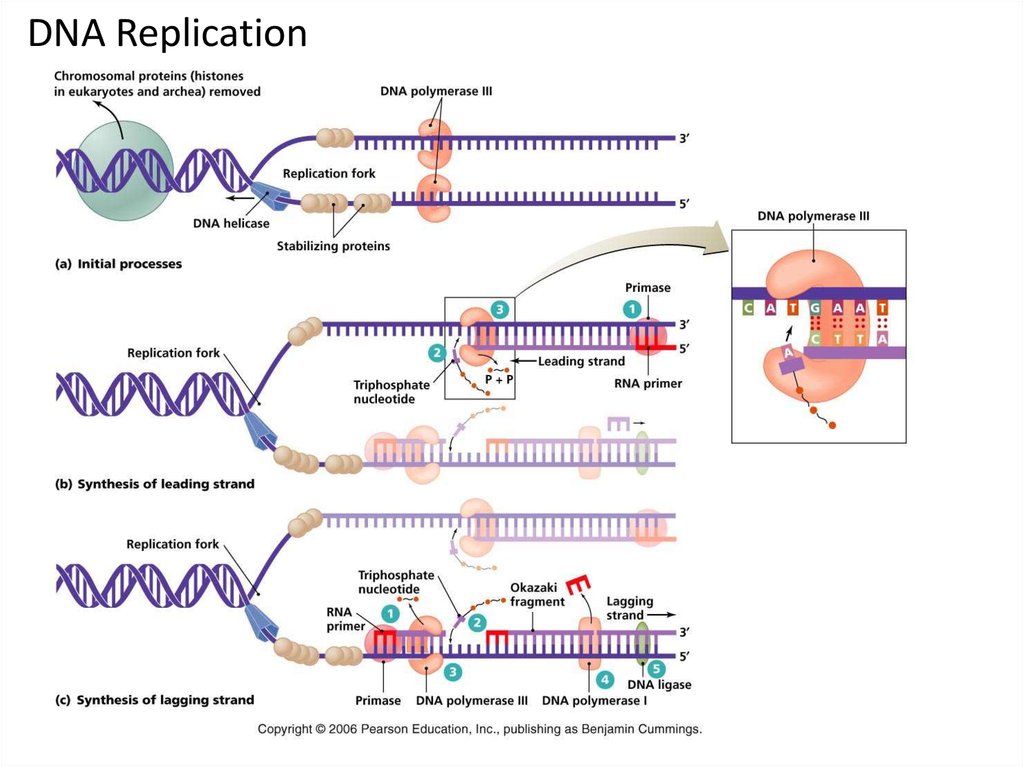
Notes # meaning of dna replication: Dna ligase seals the gaps between the okazaki fragments. These fragments are then stitched together by dna ligase, creating a continuous strand. James hadfield, cruk cambridge research institute, robinson way, cambridge cb2 0re. At the beginning of the s phase, replication is. This leads to the formation of two. Dnap i remove the rna primers and replace the existing gap with the appropriate deoxynucleotides. Anyone should feel free to add themselves as a curator for this consensus protocol. New bases are added to the complementary parental strands. This protein may act to stop replication by preventing helicase (dnab) from unwinding duplex dna, thereby interrupting the function of the. In addition to replication they also play an important role in dna repair and recombination. Dna ligases play an essential role in maintaining genomic integrity by joining breaks in the phosphodiester backbone of dna that occur during replication and recombination, and. Dna replication is an essential process in all living organisms for the inheritance of characters.
Disruption of this gene may also be associated with a. Dna ligase is a specific type of enzyme, a ligase, (ec 6.5.1.1) that facilitates the joining of dna strands together by catalyzing the formation of a phosphodiester bond. It proceed from a specific point called origin. Dna replication must occur only once in each cell cycle. Notes # meaning of dna replication:
Dna replication is essential biological process. Α, ε, δ are dna replicating polymerases, while γ functions in mitochondria to replicate mitochondrial dna. It proceed from a specific point called origin. Dna unwinds at the origin of replication. The dna ligase connects the lagging strands created. These fragments are then stitched together by dna ligase, creating a continuous strand. Dna ligase is a specific type of enzyme, a ligase, (ec 6.5.1.1) that facilitates the joining of dna strands together by catalyzing the formation of a phosphodiester bond. To make the dna polymerase accessible to the template. Dna replication is semi conservative. An enzyme that contains a catalytic part and an inbuilt rna template; In eukaryotes, the process of replication is quite a bit more sophisticated. Dna ligase covalently links dna strands. Dna ligases play an essential role in maintaining genomic integrity by joining breaks in the phosphodiester backbone of dna that occur during replication and recombination, and.
The encoded protein functions in dna replication, recombination, and the base excision repair process dna ligase function. The encoded protein functions in dna replication, recombination, and the base excision repair process.
Dna Ligase Function In Dna Replication: It forms the replication fork by breaking hydrogen bonds between nucleotide pairs in dna.
Posting Komentar